Programmer’s Digest #78
04/03/2024-04/10/2024 New HTTP/2 Vulnerability, Ivanti Rushes Patches for 4 New Flaws, Critical ‘BatBadBut’ Rust Vulnerability And More.
1. New HTTP/2 Vulnerability Exposes Web Servers to DoS Attacks
New research reveals a vulnerability in the HTTP/2 protocol’s CONTINUATION frame, dubbed HTTP/2 CONTINUATION Flood. Security expert Bartek Nowotarski reported the issue to CERT/CC on January 25, 2024. Many HTTP/2 implementations lack proper limits on CONTINUATION frames within a single stream, enabling attackers to flood servers with frames, leading to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. These frames overwhelm server memory, causing crashes or performance degradation. Unlike HTTP/1, HTTP/2 uses header fields and CONTINUATION frames to transmit header blocks. Exploiting this vulnerability, an attacker can send endless header frames, exhausting server resources. Nowotarski warns that this attack, more severe than the Rapid Reset attack, bypasses access logs and impacts server availability. Incorrect handling of CONTINUATION frames poses significant security risks, potentially leading to crashes, memory exhaustion, or CPU overload, as outlined in RFC 9113.
2. Ivanti Rushes Patches for 4 New Flaws in Connect Secure and Policy Secure
Ivanti has issued security updates for Connect Secure and Policy Secure Gateways, addressing four flaws that could lead to code execution and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
The flaws include heap overflow (CVE-2024-21894, CVE-2024-22053), null pointer dereference (CVE-2024-22052), and XML entity expansion (CVE-2024-22023) vulnerabilities. These affect various components of the mentioned products, potentially allowing unauthenticated attackers to crash services or execute arbitrary code.
Ivanti recently patched critical vulnerabilities in Standalone Sentry (CVE-2023-41724) and on-premises Neurons for ITSM (CVE-2023-46808), highlighting ongoing security concerns. CEO Jeff Abbott acknowledged the challenges, emphasizing Ivanti’s commitment to enhancing security measures.
3. Critical ‘BatBadBut’ Rust Vulnerability Exposes Windows Systems to Attacks
A critical security flaw in Rust’s standard library (CVE-2024-24576, CVSS score: 10.0 allows command injection attacks on Windows systems when batch files are invoked with untrusted arguments. The vulnerability arises from improper argument escaping in batch file invocation using Rust’s Command API. Exploiting this flaw, an attacker can execute arbitrary shell commands. This issue affects Rust versions prior to 1.77.2. Security researcher RyotaK discovered and reported the bug to CERT/CC, naming it BatBadBut. The flaw impacts multiple programming languages that use similar mechanisms. Developers are advised to exercise caution and avoid executing commands from directories included in the PATH environment variable to mitigate risks.
4. Critical Flaws Leave 92,000 D-Link NAS Devices Vulnerable to Malware Attacks
Threat actors are targeting around 92,000 internet-exposed D-Link NAS devices, exploiting CVE-2024-3272 (CVSS score: 9.8) and CVE-2024-3273 (CVSS score: 7.3). These affect legacy D-Link products, now end-of-life (EoL). D-Link advises replacement as it won’t issue patches. Exploitation could lead to arbitrary command execution, granting access to sensitive data or enabling DoS attacks. Attackers use these flaws to distribute the Mirai botnet malware, potentially hijacking D-Link devices remotely. Shadowserver Foundation recommends firewalling remote access or taking devices offline until a fix is available.
Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 warns of increasing malware-initiated scanning attacks on network devices, underlining the evolving threat landscape.
5. OAuth 2.0 flows explained in GIFs
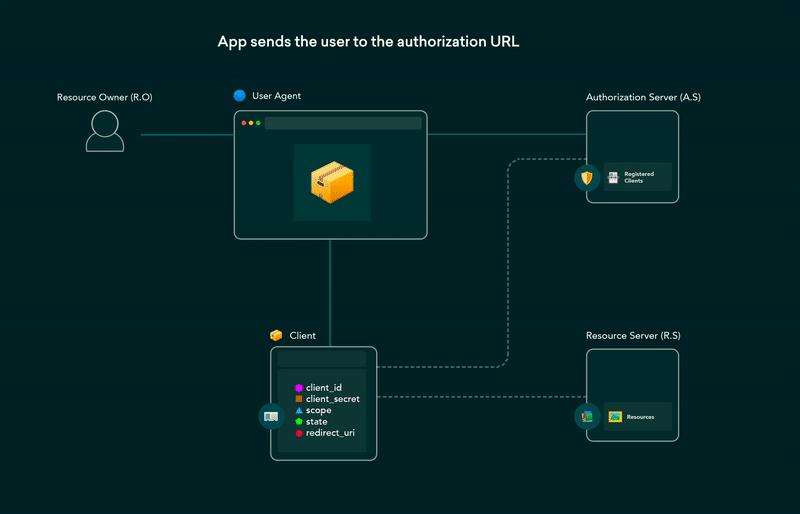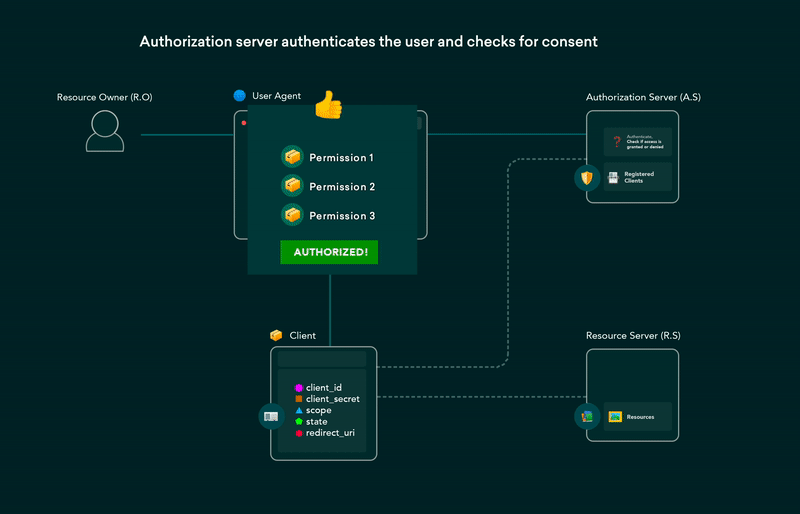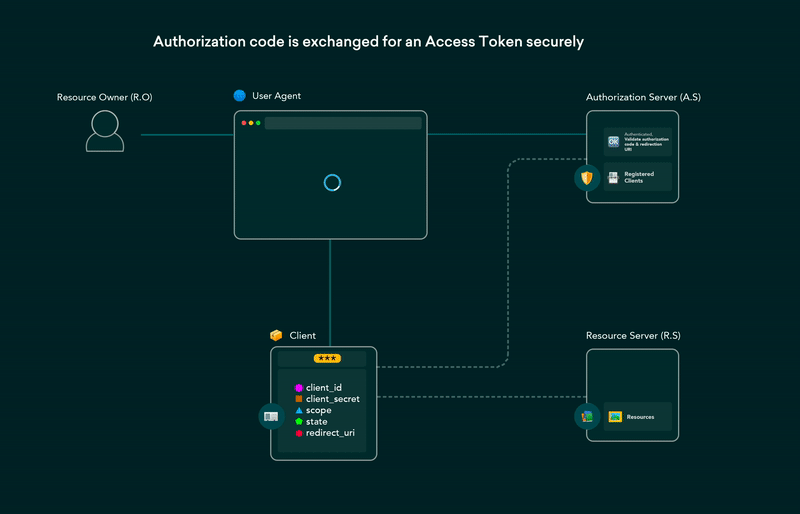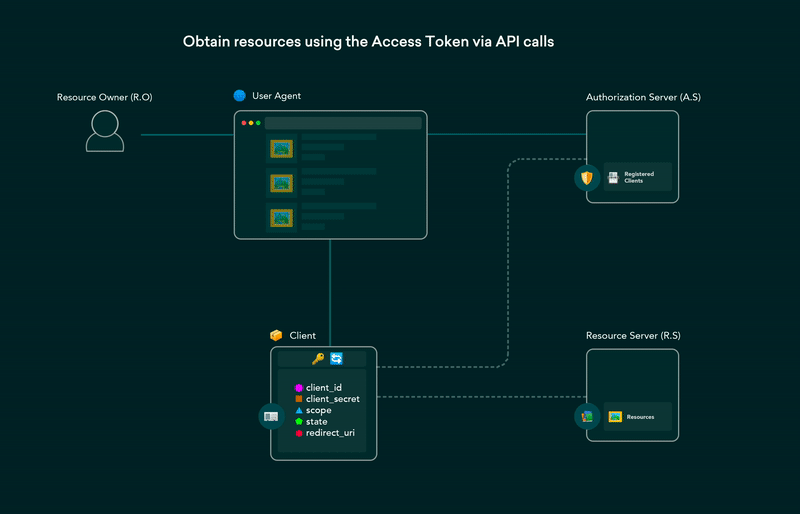
OAuth (Open Authorization) enables third-party websites or apps to access user’s data without requiring them to share their credentials. It is a set of rules that makes access delegation possible. The user gets to authorize which resources an app can access and limits access accordingly.
Post on the dev.to covering all OAuth 2.0 flows using GIFs that are simple and easier to understand. This post can be used as a cheat-sheet for future reference as well.
